Skip to the good bit
ToggleSurety bonds might sound complicated, but they’re actually straightforward financial agreements that protect businesses and consumers every day. Whether you’re a contractor bidding on a government project or a business owner applying for a license, understanding how surety bonds work can save you time, money, and potential legal headaches.
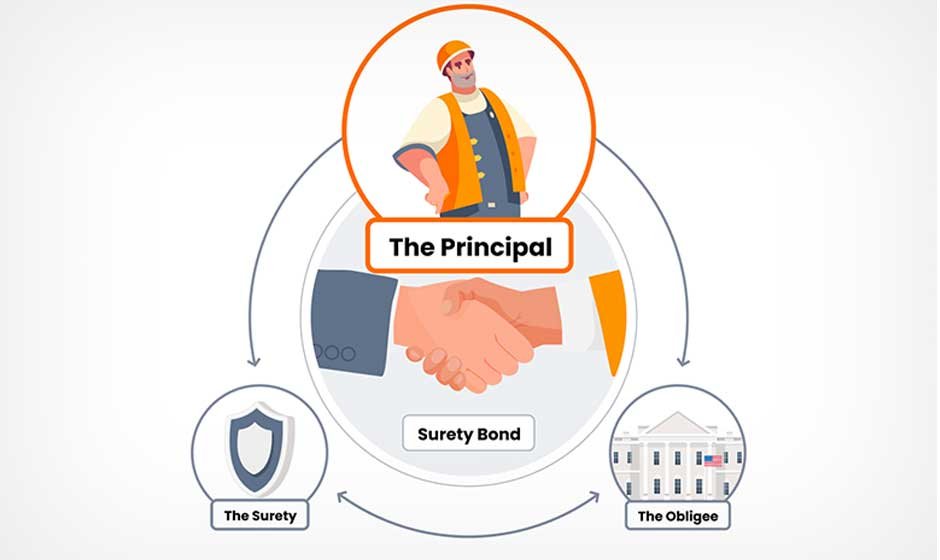
A surety bond is a three-party contract that guarantees one party will fulfill their obligations to another. Unlike insurance, which protects the policyholder, surety bonds protect the party requiring the bond. They serve as a financial safety net, ensuring that contracts are completed, regulations are followed, and consumers are protected from potential losses.
The surety bond industry facilitates billions of dollars in economic activity across Canada, from construction projects to professional services. By understanding the roles of each party involved, you’ll be better equipped to navigate bond requirements in your industry and make informed decisions about your business operations. For tailored advice and the right coverage, you can request surety bonding insurance from St. Andrews Insurance to meet your contractual and legal obligations with confidence.
The Principal: The Party Making the Promise
The principal is the individual or business that purchases the surety bond and makes a promise to fulfill specific obligations. This party is essentially saying, “I guarantee I will complete this work, follow these regulations, or fulfill this contract as promised.”
Principals come from various industries and situations. Construction contractors need performance bonds to guarantee project completion. Auto dealers require dealer bonds to operate legally. Freight brokers need broker bonds to ensure they’ll pay carriers. Court officials need fiduciary bonds to protect the estates they manage.
When a principal applies for a surety bond, they’re taking on significant responsibility. They must complete their obligations as specified in the bond terms. If they fail to do so, they become liable for any resulting damages or losses. The principal also agrees to indemnify the surety company, meaning they’ll reimburse the surety for any claims paid on their behalf.
The principal’s financial strength, credit history, and industry experience all factor into the bond approval process. Surety companies evaluate these elements to determine the risk level and appropriate premium rates. Principals with strong financials and clean track records typically qualify for better rates and terms.
The Obligee: The Protected Party
The obligee is the party that requires the bond and receives protection from it. This entity has a vested interest in ensuring the principal fulfills their obligations and stands to lose financially if the principal fails to perform.
Government agencies frequently serve as obligees when requiring contractors to post performance bonds for public works projects. They need assurance that taxpayer-funded projects will be completed according to specifications and timelines. Professional licensing boards act as obligees when requiring licensed professionals to maintain bonds, protecting the public from potential misconduct or negligence.
The obligee has specific rights under the bond agreement. If the principal fails to meet their obligations, the obligee can file a claim against the bond. This process provides a streamlined way to recover damages without lengthy court proceedings. The obligee doesn’t pay for the bond protection—this cost falls entirely on the principal.
However, the obligee must follow proper procedures when making claims. They typically need to provide documentation proving the principal’s default and quantifying the resulting damages. The surety company will investigate these claims to verify their validity before making payments.
The Surety: The Financial Guarantor
The surety company is the financial institution that issues the bond and guarantees the principal’s performance. This party agrees to step in and fulfill the principal’s obligations if the principal defaults, up to the bond’s penalty amount.
Surety companies don’t simply hand out bonds to anyone who applies. They conduct thorough underwriting processes, examining the principal’s financial statements, credit reports, business experience, and project history. This evaluation helps determine whether to approve the bond application and at what premium rate.
When a claim is filed against a bond, the surety company investigates to determine its validity. This process may involve reviewing contracts, inspecting work sites, interviewing witnesses, and consulting with experts. If the claim is valid, the surety has several options: they can pay the obligee directly, hire another contractor to complete the work, or provide other remedies as specified in the bond terms.
The surety’s investigation doesn’t end with claim payment. They’ll pursue recovery from the principal through the indemnity agreement. This might involve seizing assets, garnishing accounts, or taking legal action to recoup their losses. The surety-principal relationship continues until all obligations are satisfied.
How Surety Bonds Work: The Complete Process
The surety bond process begins when an obligee requires a bond as a condition of doing business. The principal then approaches a surety company or works through a licensed bond producer to obtain the necessary coverage.
During the application process, the surety evaluates the principal’s qualifications through a comprehensive underwriting review. They examine financial stability, industry experience, and past performance to assess risk levels. This evaluation determines whether to approve the application and what premium to charge.
Once approved, the principal pays the bond premium—typically a percentage of the total bond amount. The surety then issues the bond, creating the three-party agreement. The bond remains in effect for the specified term, during which all parties have ongoing obligations.
Risk assessment is crucial throughout this process. Surety companies use sophisticated modeling to evaluate potential losses and price their bonds accordingly. They consider factors like project complexity, economic conditions, and the principal’s track record. This careful evaluation protects both the surety company and the system’s overall integrity.
If problems arise during the bond term, the obligee can file a claim. The surety investigates promptly, working to resolve issues quickly and fairly. This might involve facilitating communication between parties, providing technical assistance, or ultimately stepping in to fulfill the principal’s obligations.
Understanding Your Role in the Surety Triangle
Surety bonds create a unique three-party relationship that provides security and facilitates business transactions across numerous industries. The principal commits to fulfilling their obligations, the obligee receives financial protection, and the surety provides the guarantee that makes it all possible.
This system works because each party has clear responsibilities and incentives to fulfill their roles. Principals must perform to protect their reputation and avoid indemnity claims. Obligees get security without paying for it. Surety companies carefully manage risk while earning premiums for their guarantees.
Whether you’re seeking your first bond or looking to better understand an existing requirement, remember that surety bonds are partnership agreements. Success depends on clear communication, proper documentation, and all parties understanding their roles and responsibilities. By working with experienced surety professionals, you can navigate bond requirements efficiently and protect your business interests throughout the process.